Insight
Heaven can wait! Bitter reality of Nigeria’s pension trap
- Starvation, death, grip elderly retirees amid economic hardship
- Broken promises, bureaucratic neglect leave pensioners in despair
- The Silent Thieves of Twilight:Arithmetic of Nigeria’s Pension Fraud
By Olatunji OLOLADE, Associate Editor
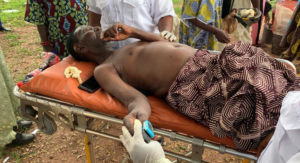
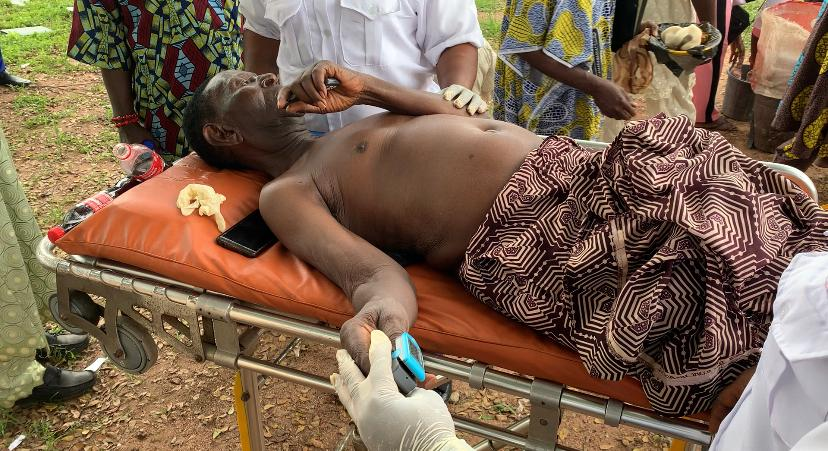
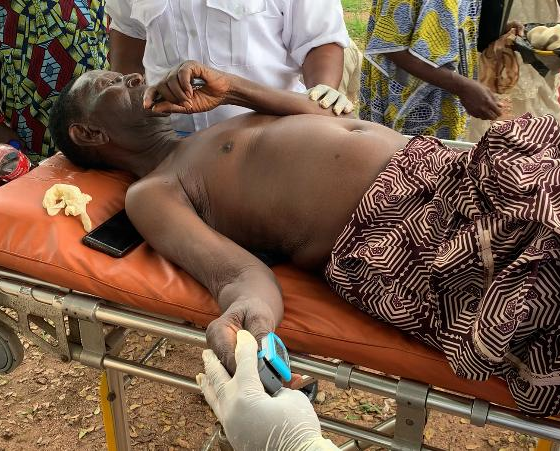
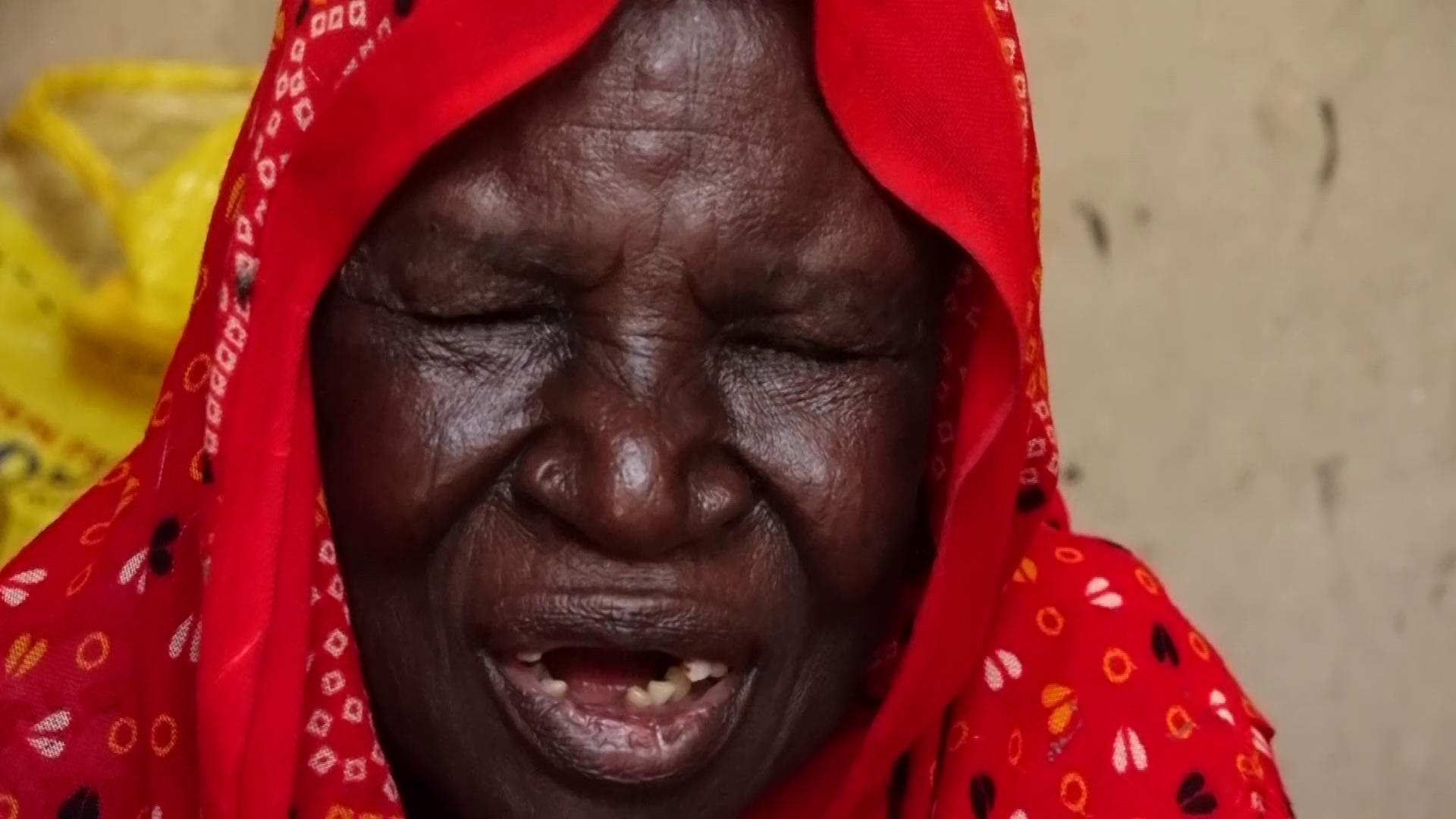
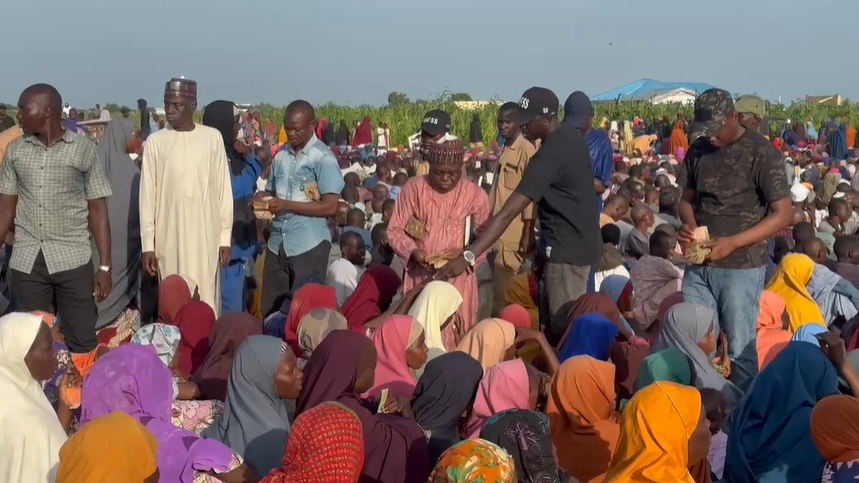
Pensioner taking first aid in Osun, after he slumped during screening exercise at the state’s pensions office.
Sunday Oboite hit the floor with a hard thud, his clatter reverberating through the large hall—a threnody for those who still clung to life, while dying to receive their pension.
At 1:20 pm, Oboite fell, not the thump of flesh on cold concrete, but the crash of hope shattering on the granite of a broken vow.
The 75-year-old had been waiting, silently, with hundreds of fellow retirees who had gathered in the dimly-lit hall of the Oredo Local Council Secretariat in Benin City, Edo State, to receive their meagre pensions after a ten-month delay.
But as the sun arched high over the Secretariat, Oboite slumped forward, his body no longer able to bear the burden of waiting.
His fellow retirees scrambled—some to help, others fleeing, as if falling was contagious.
At precisely 1:38 pm, doctors would confirm what every pensioner in that hall already knew: Oboite was dead, not from a stroke, nor from an unforeseen illness, but from starvation—starved of sustenance, of both food and dignity.
His death arrived as a brutal punctuation to the long, agonising sentence that was his final years, triggering a question that pierced the heart of Nigeria’s moral fibre: “Must the government starve its elderly to death?”
Oboite had served the government for decades, working in the Works Department of the Oredo Local Council. Like many of his colleagues, he had believed in the promise that at the end of his service, his twilight years would be spent in peace, supported by the pension he had earned. Instead, he found himself trapped in a cruel purgatory, waiting in vain for months, as hunger gnawed at his insides. The pension arrears, which had become his lifeline, dangled just out of reach, a cruel tease that would eventually cost him his life.
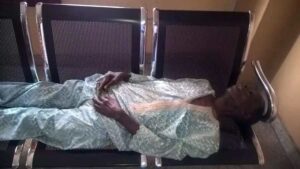
Late Sunday Oboite, 75, collapsed and died during a screening exercise for pensioners at the Oredo local council in Edo.
The morning of his death, Oboite had arrived at the secretariat at 8 am, hoping to be screened and finally paid his dues. But bureaucracy, as always, was the slowest-moving beast. After hours of waiting, pensioners were directed to a hall a hundred meters away. Oboite, too weak to walk any further, had chosen to wait behind, his body betraying him in its exhaustion. By 1:20 pm, he had collapsed. By 1:38 pm, the doctor’s cold pronouncement: Dead.
“It was hunger that killed him,” John Eweka, a fellow retiree, whispered bitterly, his voice cracking like old leather in the heat. “Many of us can no longer afford to eat. We begged for what is ours, and they denied us even that.”
Four hundred and fifty four days later, Oboite’s body still laid cold in the morgue, abandoned like the promises of the government that failed him. His family could not afford the burial costs, and his colleagues, equally impoverished, could do nothing to help. Even the eventual promise of financial support from the Edo State Governor Godwin Obaseki felt hollow, a posthumous mockery for a man who had died of neglect.

A History Written in Blood and Tears
Before Oboite, there was Olusa Ayodele, an 80-year-old man who collapsed under the weight of government indifference. Ayodele had retired from the Federal Ministry of Agriculture, only to face a fate worse than the toils of his youth. On October 10, 2011, Ayodele traveled a painful journey of hours from his village of Akunnu-Akoko to Akure, where he was due to undergo yet another “verification” for pension arrears that had long been owed. Fevered and weak, Ayodele arrived at the verification centre only to vomit twice—a grim harbinger of the end. His son, Deji, cried for help, but none came.
Like Oboite, Ayodele died waiting, his body abandoned on the bare floor for hours as his fellow retirees quietly maintained their spots on the queue, heartbroken yet hard-pressed to complete their screening.
Ayodele’s death, like Oboite’s, was a slow, bureaucratic “murder” executed in the guise of “verification” and administrative delays.
Nigeria’s retired workforce, now shadows of their former selves, suffer these in the twilight of their existence. The reality is, however, darker than any statistic could capture, with over one million retirees left stranded, awaiting pensions that may never come.

Some retirees protesting at the African Alliance Plc Lagos office over its failure to remit their pensions.
The Curse of African Alliance
Many retirees are forced to endure a life of misery and starvation as imposed by systemic and administrative failures. One of the most egregious examples of the system’s failures can be found in the recent collapse of the African Alliance Insurance Plc. Pensioners, who trusted the company with their life savings, now find themselves destitute as the company falters under the weight of insolvency.
For months, retirees flocked to African Alliance offices, hoping for a glimmer of hope. Instead, they found the doors locked, the offices deserted, and their pensions vanished into the ether. “We have been abandoned,” lamented Monsurat Idris, a retired teacher from Dopemu, Lagos. Like so many others, she had switched to an annuity plan, promised “salary for life,” only to watch helplessly as her entitlements dwindled into nothingness.
Idris recalled how African Alliance’s representatives persuaded her and fellow retirees to dump the programmed withdrawal plan recommended by the state government for the firm’s annuity plan. They even encouraged several retirees to borrow money while waiting for their entitlements. When those entitlements finally arrived, most of it vanished into debt repayment, leaving retirees even poorer than before. The once-thriving insurance firm now stands as a monument to failure, with its top executives deserting their posts while pensioners weep over unpaid claims.
Musiliu Ganiu, a retired teacher from Lagos, while reliving his nightmare with the insurer, disclosed that since March, many retirees haven’t received a dime from the firm. He lamented that African Alliance promised him and his colleagues lifelong payments. But the insurer is now in distress, having shut down its headquarters, its promises dissolving into thin air.
In August 2023, pensioners in Lagos State, under the Contributory Pension Scheme (CPS), made a desperate appeal to Governor Babajide Sanwo-Olu, to come to their aid. In a letter dated August 20, 2023, the Nigerian Union of Pensioners (NUP), Lagos State Chapter, lamented their unpaid pensions dating back to 2007, leaving retirees impoverished.
Stripped of gratuities and forced to subsist on meagre payments, many like a former Director on grade level 17, now receive only N70,000 monthly, while lower-level workers earn as little as N12,000—or none at all in the case of those on grade levels 1 to 4.
“We receive an average of ten notifications of death of our members on a monthly basis,” the union wrote, underscoring the severity of the situation. They attribute these deaths to the economic hardship faced by retirees, who are unable to keep up with rising living costs, especially in light of the recent fuel subsidy removal.
The letter, signed by the NUP’s Chairman, Omisande Michael and General Secretary, Olagbaye Johnson, included a plea for immediate action, including the urgent payment of outstanding pensions dating back to 2020, a review of the pension payment system, and the reinstatement of gratuity for all categories of workers under the CPS.
Subsequently, the Lagos State Governor, Babajide Sanwo-Olu, in a tweet on February 11, 2024, announced that Lagos would begin payment of N3.1 billion to over 1,000 pensioners under the Contributory Pension Scheme (CPS).
Abebi Adebola, a retired school administrator and Headteacher in Lagos said that, so far, Lagos State has performed most commendably among the 36 states of the federation, in the way it treats its pensioners. Save for some occasional hiccups, retirees receive their money at due time.
According to her, some of her colleagues who retired in 2012 were luckier as they received 50 per cent initial lump payment of their entitlement in 2013, one year after their retirement. However, retirees like Adebola, who retired in 2015, had to wait for a gruelling 46 months before they received their gratuity. When they did, they were paid a paltry 25 percent of their entitlement.
The scale of the tragedy stretches far beyond individual stories. In Kwara State, over a million pensioners, precisely 1,126,000 retirees died between January 2015 and February 2017, according to the state chapter of the National Union of Pensioners (NUP) – a staggering toll that reflects the sheer depth of the crisis.
The life of a Nigerian pensioner is indeed, one bitter struggle, where survival hinges on a meager stipend of N500, N10,560, N25,000, or at best, N70,000 per month. Even this paltry amount arrives unpredictably. “The pension offers little succor,” laments Florence Alogba, 62. “It is never enough, especially with the rising cost of food.” The delay in payment compounds the hardship. “By the time the stipend comes,” said Foluso Okin, a retired principal, “it goes toward debts—medical bills, school fees, loans. We never enjoy it. They said a teacher’s reward is in heaven. But I want my reward on this earth.”
For some, the burden of an unemployed family adds to the weight. Idowu Ojo, a retired teacher, recounted the anguish of his unemployed sons: “My daughter’s husband works, but the whole family depends on her. We try not to be a burden, but the government’s failure forces our hand.”
Beyond the unpaid pensions, retirees face another torment: corruption. In southwestern Nigeria, retired teachers must bribe pension staff to process their files. “We pay N50,000 just to have our files treated,” revealed a retired primary school teacher, pleading anonymity.
Worse still is the Ebonyi State scandal, where extortionists in the audit department reportedly demanded money to process the files of retirees. One of the retirees who was not pleased with the new arrangement, Benedict Anyigor, said that he had already paid N50,000 but his file was withheld by the accused officials of the State’s Audit Department.
“I was supposed to be paid N4,787,081. Out of this amount, government has paid me N800,000 but one of the officials in the state audit and his colleague who have been processing my file for payment, said I should settle them with 200,000 out of this amount for immediate payment or my file will not be sent to the Head of Service for the payment.
“I have already given them N50,000 out of the N200,000. I told them that I will pay the remaining N150, 000 after receiving full payment of the gratuity from the government which they have started paying. But he increased the amount of settlement to N500,000 and insisted that I must pay him the amount before he releases my file to the Head of Service for the payment and I don’t have the amount. I retired as a Level 8, Step 15 officer at the General Hospital, Onueke in Ezza South Local Government Area of the state,” he said.
Reacting to the allegations, the state’s Auditor General at the period, Innocent Nweda, vowed to dismiss the culprits. He promised to investigate the alleged scandal stressing that in 2012, about four principal members of staff of the Audit were dismissed for a similar crime.
A larger gale of corruption sweeps through the pensions office of the Federal Civil Service. Nigerians won’t forget in a hurry, the scandalous case of Abdulrasheed Maina, the former Director of the Customs, Immigration, and Prisons Pensions Office (CIPPO) and Chairman of the Pension Reform Task Team (PRTT). In 2013, Maina fled the country after being implicated in a N2.1 billion pension fraud by the EFCC. Despite public outrage, he was secretly reinstated and promoted under former President Muhammadu Buhari’s administration, only to flee again to avoid prosecution.
Maina was eventually sentenced to eight years in prison after a two-year trial. Justice Okon Abang criticised the United Bank of Africa (UBA) and Fidelity Bank, accusing them of being “conduits” for the fraud and suggesting they should have been charged. The court found that Maina used fake accounts, with the help of relatives in the banking sector, to siphon funds from pensioners, many of whom died in poverty.
Justice Abang condemned Maina’s lavish lifestyle, noting he lived in luxury abroad, while pensioners suffered. He emphasised that Maina’s salary of just over N300,000 could never have amounted to the N2 billion he stole, calling the case a reflection of the moral decay in society. The judge urged for national reform and stronger action against dishonesty.
And still, the system remains unchanged. The National Pension Commission (NPC), created to oversee the Contributory Pension Scheme (CPS), has failed to enforce its own regulations. Many states have not even adopted the CPS, instead continuing under the archaic Defined Benefits Scheme (DBS), where pensions are either delayed or denied outright.
The promises of reform—like those made by African Alliance—ring hollow in the ears of retirees. NAICOM, the industry regulator, has issued ultimatums, demanding that pension fund administrators clear their debts and settle arrears, but the threats go unenforced. Instead, retirees are left to live—or die—without the money they were guaranteed.
It is a nationwide plague, a systemic failure that leaves millions of retirees in the grip of hunger, illness, and despair. The Contributory Pension Scheme (CPS), introduced in 2004 and amended in 2014, was supposed to bring transparency and security to the retirement process. Yet, 20 years later, the reality has fallen far short of that promise.

Some members of the Nigerian Union of Pensioners during a protest over non-remittance of their pension in Lagos.
The Arithmetic of Pension Fraud in Nigeria
The arithmetic of pension fraud in Nigeria unfolds like a tragic tale of exploitation, where Pension Fund Administrators (PFAs) weave intricate schemes to rob pensioners of their hard-earned savings. These institutions, entrusted with securing the future of retirees, instead cloak their actions in secrecy, siphoning wealth from the vulnerable. To unravel the mechanisms by which they prey upon the unsuspecting – hidden behind veils of fees, mismanagement, and outright theft – is to embark on a jarring journey into the bowels of an arithmetical con.
Beneath the surface of every pensioner’s account lies an unseen hand, quietly taking its due, argued Khadijah Ilemobaye, an Actuarian scientist cum insurance auditor. Explaining further, she said, a pensioner, with ₦10 million in savings, unknowingly surrenders 1.5% of that sum each year—₦150,000 in annual fees that slip through the cracks of undisclosed charges. Over a decade, this amounts to ₦1.5 million, silently drained without the pensioner’s knowledge, a slow bleed of their future security.
The PFAs, like the proverbial masters of illusion, invest pensioners’ funds in low-yield government securities. While these investments generate meager returns, the PFAs impose high management fees, further eroding the value of these already modest gains. Imagine a pension fund of ₦5 million, invested in a bond yielding a mere 6%. The pensioner earns ₦300,000 per year, yet the PFA takes 2%—₦100,000—as its fee. The pensioner is left with only ₦200,000, believing the returns are better than they are, while the true cost is hidden beneath layers of financial jargon and opaque reports.
In the dark recesses of the system, corrupt officials conjure “ghost pensioners” into existence. These phantom figures, fictitious names on payrolls, are used to divert vast sums of money. A PFA managing 100,000 real pensioners might fabricate 10,000 ghost pensioners, each assigned ₦500,000 in fraudulent pensions. In this spectral arithmetic, ₦5 billion vanishes, spirited away into the coffers of those who feed on the trust of the system, leaving the pension fund diminished by this insidious scam.
Time, in the hands of the PFAs, often becomes a weapon of control as payments due to pensioners are deliberately delayed, extending the period during which the PFA controls the funds. A pensioner awaiting ₦5 million may face a delay of six months, during which the PFA earns an 8% annual interest. In this short span, the PFA collects ₦200,000 in interest, profiting from the pensioner’s enforced patience. This delay not only disrupts lives but compounds the injustice by allowing the PFA to gain from withholding what rightfully belongs to another.
With monthly contributions flowing steadily, some PFAs quietly divert portions into their own pockets. A pensioner contributing ₦50,000 each month may find that ₦10,000 is secretly rerouted to fraudulent accounts. Over 10 years—120 months—this diversion amounts to ₦1.2 million stolen from a single pensioner. With 10,000 pensioners in their grasp, the PFAs can embezzle a staggering ₦12 billion, a grand theft concealed in the monotony of monthly deductions.
For some pensioners, the final blow comes at the moment of retirement. The gratuity, the lump sum meant to provide for their twilight years, is intercepted. A group of retirees expecting ₦1 billion in gratuities may find only half paid out, as corrupt officials siphon away ₦500 million. The pensioners, left with half their entitlement, face a future diminished by the greed of those entrusted with their care.
For one pensioner, the toll of these fraudulent practices is devastating. Over a decade, they lose: ₦1.5 million in hidden administrative fees, ₦1 million in excessive investment charges, ₦1.2 million siphoned from their contributions, ₦200,000 lost to delayed payments. In total, ₦3.9 million is stolen from a single pensioner over 10 years. Multiply this across thousands, and the scale of the fraud balloons into billions of naira—an unfathomable betrayal of trust.

Some pensioners protesting over their unpaid entitlements in Lagos.
Nigeria’s Pensions Animal Farm: Four legs good, two legs bad
Like the tidal waves that slowly erode the shore, Nigeria’s pension crisis has been silently consuming its elderly for decades. The promises that once gleamed like golden dreams have become rusted, hollowed out by legal loopholes, hidden charges, and predatory practices. Nowhere is this betrayal more stark than in the government’s imposition of a shocking 25% cap on initial withdrawals, a cruel twist that leaves retirees with only a quarter of the savings they’ve painstakingly accumulated over decades.
The full promises of a dignified retirement dissolve like fog at dawn, leaving only a fraction of the anticipated savings for the elderly to live on. Imagine spending decades working, contributing to a pension fund, believing in the promise of security, only to discover that when the moment comes to access your savings, you are handed a mere quarter of what you are owed. The remaining 75%? Locked away, dripped out in agonisingly small sums over the years.
Introduced under the guise of ensuring long-term financial stability, the 25% cap has instead become a death sentence for retirees. While pensioners who spent about 35 years in the service of their country wallow in abject poverty occasioned by their inability to access their benefits, former governors and deputies—who served for a mere four or eight years—are ushered into retirement with lavish gifts, the likes of which would make kings envious.
Until recently, Lagos State stood as a stark example of this paradox. Enshrined in the Public Office Holder (Payment of Pension) Law No 11, within the official Gazette of 2007, lies a provision that guarantees a governor, upon leaving office, a lifetime pension equal to the full salary of the sitting governor—that is, N7.7 million annually. The former governor is also granted free healthcare for himself and his family, six brand-new cars every three years, and an array of allowances fit for royalty: 300% of the annual salary for furniture (N23.3m), 10% for house maintenance (N778,296), 20% for utilities (N1.5m), and 30% for car upkeep (N2.3m).
But the largesse doesn’t end there. A former governor enjoys the luxury of an entertainment allowance (N778,296) and a personal assistant earning a quarter of the governor’s own salary (N1.9m). Domestic workers—a cook, a steward, a gardener, and more—are placed at their service, with their positions even made pensionable. For security, eight policemen and two state security officers stand sentinel for life.
In the wake of protracted outrage over the bumper package, however, the Lagos State House of Assembly, in 2022, amended the state Pension Law for former governors and other political office holders, reducing their benefits and emoluments by 50 per cent. The House expunged the provision of houses in Abuja and Lagos for former governors, Sequel to the presentation of a report by the House Committee on Establishment, Training and Pension.
It further recommended a reduction in the number of vehicles to be made available to former governors and their deputies as the House Speaker, Mudashiru Obasa, suggested that the former governors should get two vehicles (a car and a van) instead of the three recommended by the committee, and advised that the cars be changed every four years instead of the three years previously recommended by the report.
Elsewhere, Delta State offers its ex-governors a fully furnished duplex in any state of their choosing, and also full medical care for their families, two vehicles (including a utility car) every two years, and a protective entourage of armed officers. Fifteen days of annual vacation in any part of the world are but another pearl on this string of luxurious benefits. Meanwhile, in Kano, the former leaders are gifted with a six-bedroom mansion and healthcare for life, while Ekiti provides its retired governors with a plush five-bedroom duplex, two cars, a pilot vehicle to be replaced every three years, and 300% of the annual salary for furniture.
In Rivers State, Celestine Omehia, whose governorship was nullified by the Supreme Court, still walked away with a princely sum of N695 million in entitlements.
Across at least 22 states, from Oyo to Zamfara, Kwara to Rivers, similar stories echo: ex-governors and their deputies luxuriate in the fruits of their brief tenures, their coffers brimming with the spoils of jumbo pensions, while civil servants who toiled for decades in the nation’s service languish, unpaid and forgotten.
At the federal level, the story turns no less extravagant. In the 2023 budget, a staggering N13 billion was earmarked for the pensions of former Presidents, Vice-Presidents, Heads of State, retired chiefs of service, permanent secretaries, and heads of agencies. There is no record, none at all, of any of the recipients lamenting unpaid pensions, no whisper of delay in their vast entitlements.
Meanwhile, the retired civil servants, who dedicated 35 years of their lives to the nation, wait in vain for their dues. Against the backdrop of the malady, the scales of justice occasionally tilted on the side of truth. In 2019, the Federal High Court in Lagos, under the gavel of Justice Oluremi Oguntoyinbo, declared these life pensions for ex-governors and deputies illegal, immoral even. The Attorney General was ordered to take swift legal action to abolish these laws and recover the ill-gotten funds.
Previously, in the Socio-Economic Rights and Accountability Project (SERAP) v Attorney-General of the Federation, (Suit No. FHC/L/CS/1497/2017 and Alhaji Garba Umar v Taraba State Government (Suit No: NICN/JOS/26/2016, the Federal High Court and the National Industrial Court declared as null and void the payment of pension and gratuity to former governors and deputy governors.
Senators Gbenga Daniel and Ibrahim Dankwambo, both former governors, have also directed the governments of their respective states, Ogun and Gombe respectively, to stop paying them a governor’s pension since they are currently receiving salaries and allowances in the National Assembly just as the governments of Kwara, Imo and Zamfara States have abolished the payment of the controversial pensions to their former governors and their deputies.
“We call on other state governments to abolish the pension as soon as possible. Nigeria can no longer afford to pay scandalous pension to ex-governors while workers are owed arrears of meagre pensions,” said Senior Advocate of Nigeria, Femi Falana (SAN).
However the payment of the lavish pensions for ex-governors and deputies continue unabated.

Retirees in Bayelsa march on the streets to protest their unpaid entitlements.
Navigating the Trap
On September 17, 2024, the National Pension Commission (PenCom) announced that total pension assets have reached N20.79 trillion. However, only seven states—Lagos, Kaduna, Delta, Ekiti, Osun, Edo, and Jigawa—and the Federal Capital Territory (FCT) have fully implemented the Contributory Pension Scheme (CPS).
PenCom’s Acting Director General, Omolola Oloworararan, highlighted the steady growth of pension funds, noting that states had remitted over N236.7 billion between January 2020 and mid-2024. She emphasized the benefits of adopting the CPS, such as access to pension funds for infrastructure projects through state bonds. Lagos, Niger, Osun, Ekiti, and Delta have successfully issued state bonds backed by pension funds, with projects like the Lekki-Ikoyi Bridge in Lagos benefiting from this funding.
PenCom, she said, is focused on engaging 26 states with CPS or CDBS laws that have yet to begin implementation, aiming to ensure that all retirees receive timely benefits. The commission is also working to resolve accrued rights payments and ensure pension increments in line with the Nigerian Constitution, stated Oloworararan.
Regardless of her sunny assurances, Oloworararan may find it difficult convincing millions of pensioners caught in a maelstrom of unpaid benefits and neglect.
A higher proportion (70%) of the retired, aged, and ageing population in Nigeria earns N50,000 per month or less or nothing, according to a study sample by Dataphyte and JAIRAA. At this income level, the retired, aged, and ageing (RAAs) live below the global poverty line. According to the World Bank, the poverty line is estimated at $2.15 or N3,190 per day (at N1,484 per dollar).
For those nearing retirement, the lesson is clear: vigilance is the only armour. Nigerians must demand transparency from pension fund administrators, refusing to be lured by the false promises of higher returns, advised Usman Shoyode, an insurance auditor and financial risk analyst. To PFAs, he suggested that retirement savings must be diversified and spread more transparently across multiple funds to mitigate the risk of loss.
Above all, the 25% cap must be challenged, both in the law courts and in the hearts of the people, who must demand that their government provide the full measure of what they are owed.
It is also very essential to research and choose pension fund administrators (PFAs) carefully. Avoid companies with a history of delayed payments or unresolved claims, and opt for those with a proven track record of stability. Furthermore, retirees may consider diversifying their retirement investments. Relying solely on the pension system can be a recipe for disaster, as the stories above illustrate. Personal savings, real estate investments, or even small-scale business ventures can provide additional security in a country where government promises are often as fragile as the lives they are meant to protect.
As the sun sets on the lives of those who once carried Nigeria on their shoulders, it becomes ever more urgent for the nation to confront the grim reality of its pension system. Because for every Ayodele who falls, and for every Oboite whose heart gives out, the very soul of the nation weakens. It was on a sunless day that they both fell, into the abyss of a failed promise. Their last breaths churning against the silence of those who watched their struggle and did nothing. The aged civil servants, who once who tilled the earth and built roads for the living, got railroaded, destitute and disenchanted, into an early grave.
Environment
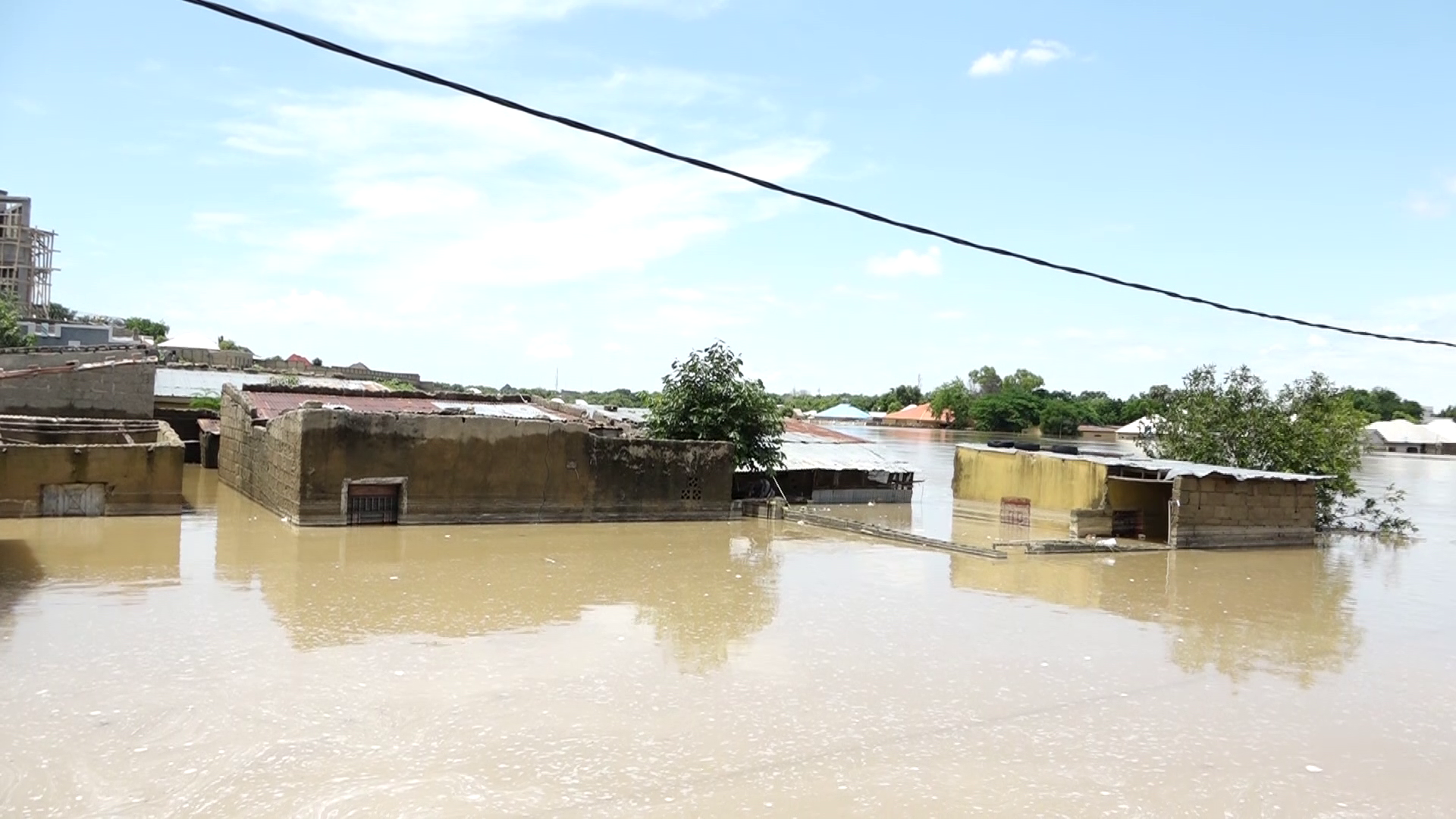
Lost anchors: Maiduguri women bear bitter burden of September flood

 Lost anchors: Maiduguri women bear bitter burden of September flood
Lost anchors: Maiduguri women bear bitter burden of September flood
- The flood took their homes, but it is hunger that seals their fate
- At the mercy of predators: Sad fate of widows, mothers, daughters adrift in wreckage of an unforgiving deluge
- Stripped of family, hope, their only constant is the struggle to survive
Environment
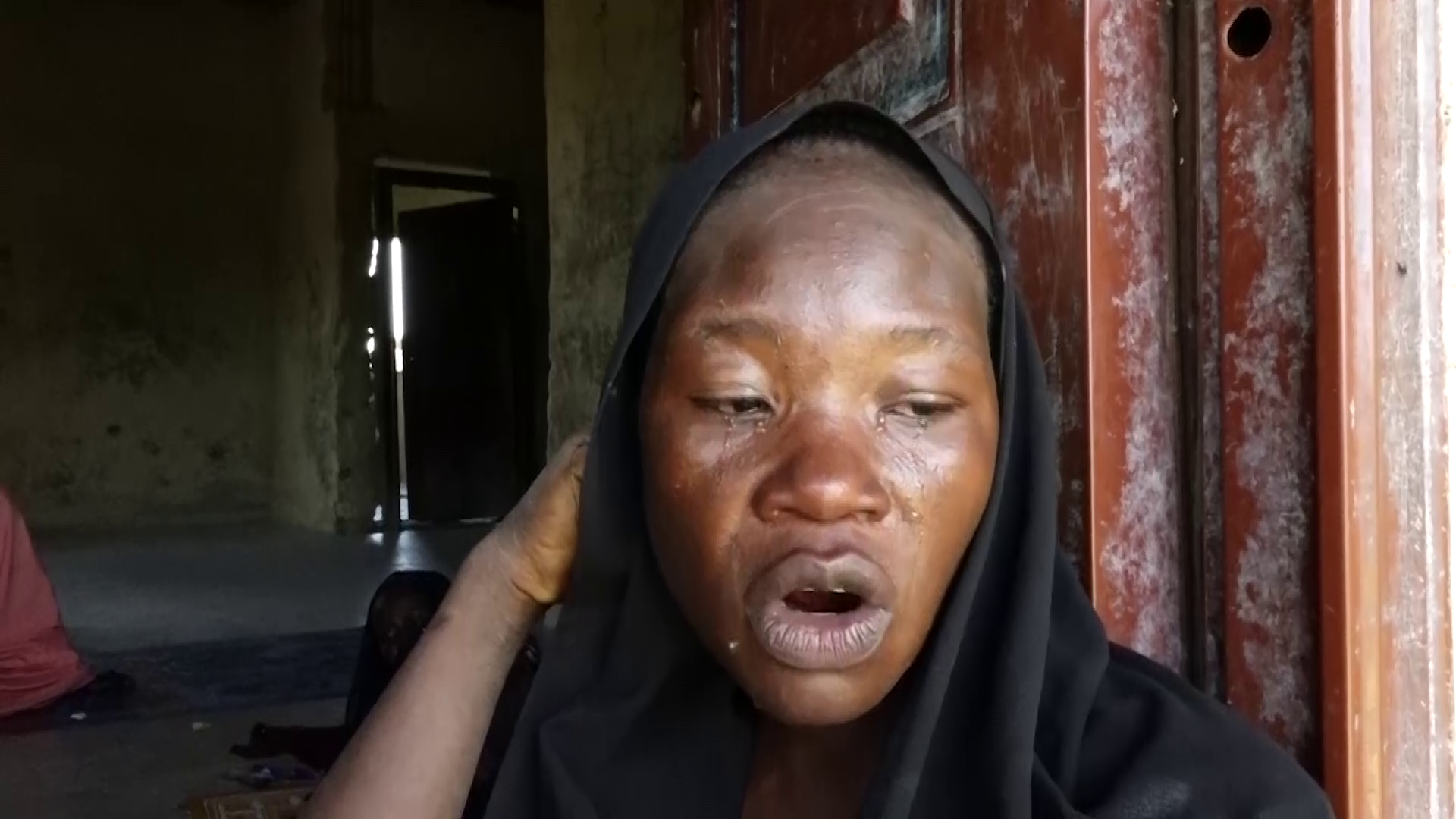
It smelled like death: How flood disaster erase Borno’s blind elderly


- In belly of the beast: Haunting reality of Zara Aji, others’ amid Maiduguri’s reptilian waters
- As waters recede, PWDs wander through a world they cannot see, that will not see them
- Betrayed by policy, drowned by nature: Non-inclusive laws leave PWDs gasping for survival
By Olatunji OLOLADE, Associate Editor
The flood stole silently at first, slithering through the streets of Gwange like a reptilian beast. Until it got to Zara Aji’s home. By the time Aji stirred in her bed, she was soaked to the pants. The Alau Dam had collapsed hours before, spilling with nature’s pent-up rage. It was 3 a.m. when the water began its slow, fearsome crawl into her abode.
The cold splash from her feet up to her midriff startled her fully awake, but her blindness kept her trapped in a black sea of panic. Aji could hear the roar of the waters outside, and its chilling hum inside her room. She sat, helpless, dreading the rising tide of doom. At 83, her body was frail, her sight stolen by the passage of time. As the flood rose to her waist, the house groaned around her, listing to the weight of the water gushing in from every crack and crevice. The room was no longer hers but a watery tomb. And yet, in that critical moment, salvation came in the form of her grandson’s love.
Mohammed, having heard the chilling hiss of the flood as it licked the edges of their compound, was up in an instant, wading through the house, daring the surge in search of his granny.

A debt of love carried through cold waters
Mohammed found Grandma Aji shivering in bed. Instantly, he lifted her frail body onto his back. The weight was light, but the task heavy, but the teenager waded through the depths of the flooded house, each step a battle against the current that sought to pull them both under.
Tears slid down Grandma Aji’s cheeks, as she clung to her grandson, the poetic resonance of the moment sinking into her heart. In that moment, he was no longer the toddler she rocked to sleep on her back, singing soft lullabies. The roles were reversed. The grandson was now the saviour and protector, bearing his grandma to safety through dangerous waters.
Aji could feel the waters splashing against the boy’s chest. She could hear him grunt as he fought to keep them moving. And in the darkness, as the deluge threatened to take everything from them, there was a strange, haunting beauty in the way love had come full circle.
Mohammed hastened out of the house before its walls crumbled. There was no turning back. The water seemed endless. But they moved through its depths, slowly but steadily towards London Chikki. The journey was treacherous, but the boy didn’t falter. He held tightly to his grandmother, knowing that in that moment, he was carrying more than just her frail body—he was bearing a lifetime of memories, of love, of shared history.
Into the shallows, but not to safety
They sought refuge in the London Chikki area, but the flood had not spared it either. The waters were still rising, the current still swirling to pull them both under. “We walked again,” Aji recalled, her voice frail with grief and exhaustion. “We walked until we reached the main road.”
For three days, they stayed on that road, waiting for the waters to recede, like so many others whose lives had been uprooted by the flood. They watched the sky for signs of hope, but none came.
Hunger gnawed at their stomachs, and the cold seeped into their bones. They were far from safety, but at least they had survived.
Eventually, they sought refuge with Aji’s brother, who took them in until the waters receded.
As the floodwaters receded, the destruction left behind was staggering. What they returned to was not a home but a hollow shell of what once was. Aji’s home was gone, reduced to a pile of broken walls and sodden memories. Her clothes and few possessions had been swept away in the torrent, leaving her destitute.
“The government didn’t provide anything for us,” she said, her voice carrying the weight of betrayal. “We heard there was support, but it never came to our community.”
The flood had claimed so much—her home, possessions, and sense of security—but at least it had not taken her.
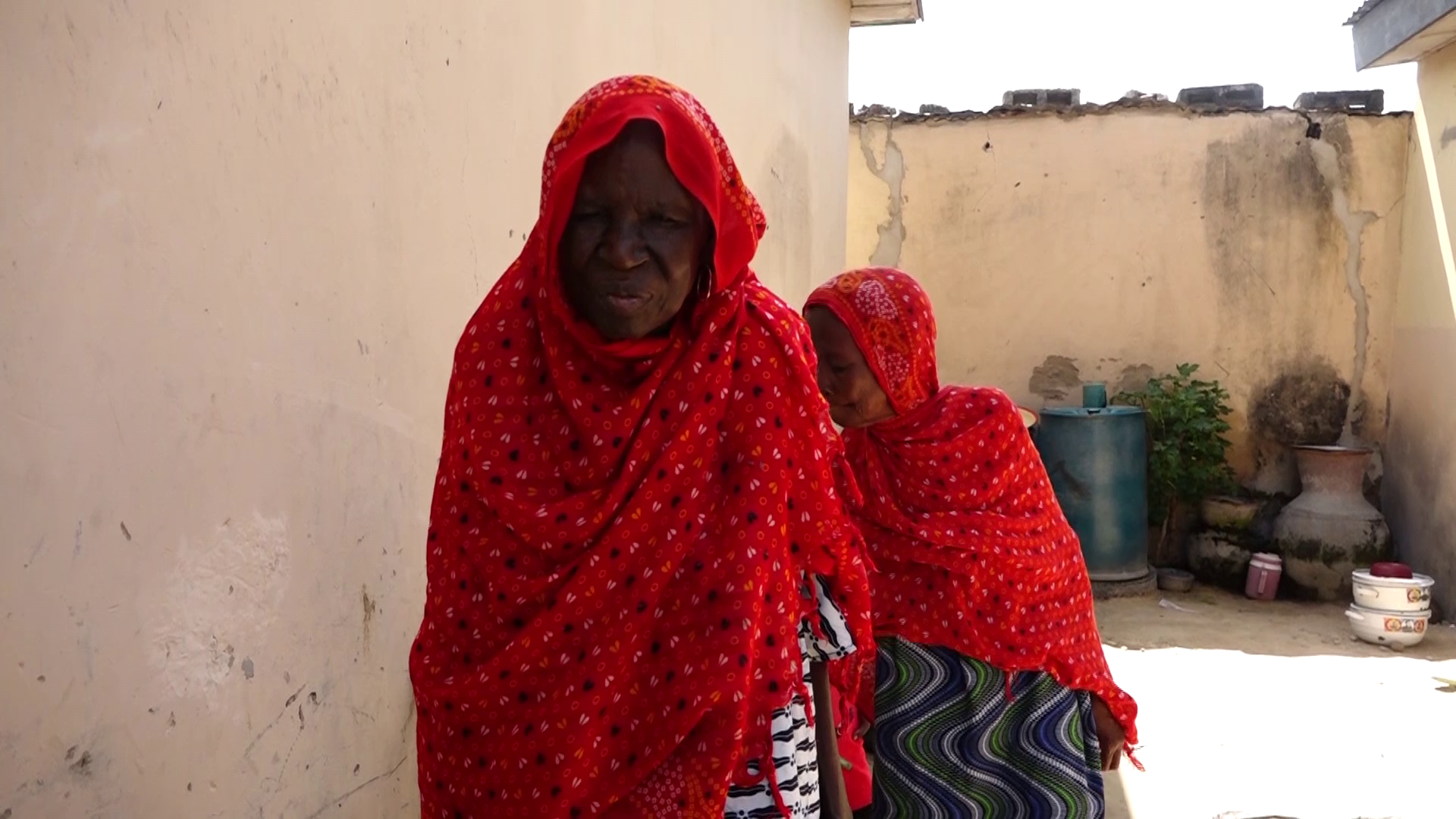
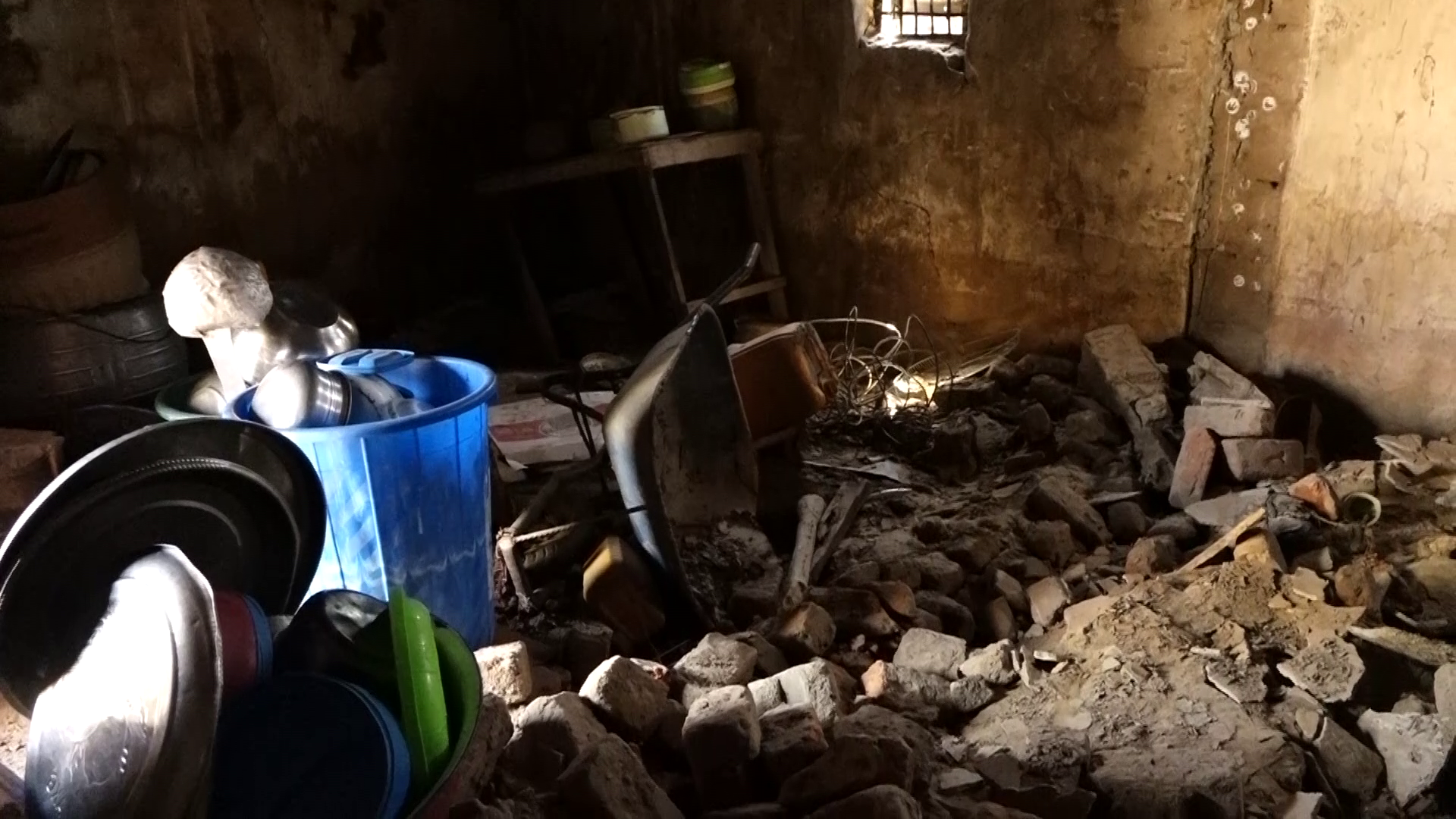 The flood destroyed visually impaired Zara Aji’s home, leaving in its wake a pile of rubble.
The flood destroyed visually impaired Zara Aji’s home, leaving in its wake a pile of rubble.
Lost in the torrent: Stories of the invisible
Aji’s experience is one among several narratives of persons with disabilities (PWDs). And they all resonate with a deafening chill. For most elderly PWDs, the flood was not just a natural disaster but a test of survival against unimaginable odds. As the waters rose and people fled, PWDs who could not see the danger approaching, were left behind.
Not all were so fortunate, like Aji. On the same night that her grandson rescued her, Safinatu Bala and her friend, Seyidatu, got lost in the waters. Widows both, the two women reportedly lived side by side in Gamboru, their lives intertwined by friendship and a shared hardship of visual impairment.
When the flood came, they clung to each other, and wailed for their neighbours to rescue them from the fury of the rising water. But in the chaos, they got separated and swept apart. By morning, neither woman could be found. No one knows if they are still alive, groping around some distant tree or rock, or if they had succumbed to the flood’s cold embrace.
On his part, Iliyasu, an 84-year-old visually impaired and internally displaced person (IDP), told his fellow PWD and co-squatter around the Monday Market, in Maiduguri, to leave him. “I have lived through too many floods. I will survive,” he said. “But if this is to be my end, then so be it.” His words were a stark reminder of the quiet desperation that clung to several PWDs amid the deluge. Like Bala and Seyidatu, Iliyasu hasn’t been seen since September 10.
For many PWDs in Maiduguri, the flood was a cruel reminder of their vulnerability. They could not see the rising waters, or gauge the danger until it was too late. Volunteers and aid workers, in their rush to evacuate the able-bodied, overlooked those who could not flee on their own, noted Zulfatu Adamu, a Maiduguri-based aid worker. And so, the blind and disabled were left behind, their cries for help drowned out in the snarl of the flood.
Alau Dam: The collapse that unleashed a torrent of sorrow
The flood that swept through Maiduguri and the surrounding areas was not an act of nature alone. It was the result of years of neglect and mismanagement, of warnings ignored and repairs postponed. Thus on the night of September 9, 2024, after days of torrential rain, the Alau Dam finally gave way, its weakened structure crumbling under the weight of the water.
At the dam’s collapse, Maiduguri experienced its most severe flooding since 1994. Severe flash flooding submerged the Maiduguri Metropolitan Council (MMC) and Jere Local Government Area (LGA), displacing hundreds of thousands of people, including PWDs, at the height of the agricultural lean season’s food and nutrition crisis.
In a statement titled, “Flooding Alert for River Bank Residents,” the Commissioner for Information and Internal Security, Prof. Usman Tar, called for the immediate evacuation of affected areas, and urged residents to follow designated evacuation routes for their safety. However, a major blindspot of Borno’s rescue plan was the safe evacuation of PWDs in the flood prone areas.
When the waters surged, the rush to evacuate became a race against death. For most, it was a panicked dash through roads slick with mud, toward whatever safety they could find. The waters ravaged villages, farmlands, and human lives alike—but hidden in the narrative of loss was the quieter, deeper anguish of several elderly PWDs. For blind PWDs like Aji, Bala, Seyidatu and Iliyasu, the flood was a manifestation of their deepest fears.
Visually impaired, their world had always been one of shadows, but the deluge brought with it an unprecedented darkness that they could not navigate. In the chaos, they were left behind, like mere shadows on the periphery of a frantic exodus.
Bitter streets, bitterer shelter
As the deluge persisted, survivors sought refuge at emergency shelters, filled to capacity. “Before the flood, I lived with my niece. She invited me to squat in her home after her husband died. On the night that the flood destroyed our home, I couldn’t sleep easy. I woke up and everywhere smelt like death. But it was the flood, and it almost drowned me and Rekiya (one her niece’s kids). We fled and now have to live on the streets. We depend on alms to survive,” lamented Fatima Yagana. The 74-year-old visually impaired widow, having been rendered homeless and destitute by the flood, now lives on the streets with her niece, Ayisatu, and the latter’s two kids because they couldn’t stay at the Gwange 1 emergency shelter due to the unsanitary conditions.
The crowded shelter, like so many others, offered no sanctuary. Forced to live within the squalor, the stench of human waste clung to the air, rendering the already unbearable heat suffocating. “The toilets smelt really bad,” Yagana lamented. Deprived of sight, her only solace was the breath of air she could steal from the shelter. So, the 74-year-old chose the streets—preferring the rough ground and open sky to the claustrophobia of an unsanitary refuge.
Yet on the streets, hunger stalked her and her niece’s children like a wolf at their heels. The flood had not only taken their home but stripped them of any dignity they once had. Handouts became their only means of survival, each day a bitter fight for morsels of food, each moment a testament to the indignity of abandonment.

A humanitarian void
The Borno State Government, alongside humanitarian agencies, scrambled to provide aid. Yet, amid the efforts to register and assist the displaced, the specific plight of PWDs slipped through the cracks. In total, more than 2,500 people with disabilities in the flood prone areas were directly affected by the flood, many of them left stranded in their homes as the waters rose, with over 150 missing or presumed dead, according to the National President of the Joint National Association of Persons with Disabilities (JONAPWD), Abdullahi Ali Usman.
The figure quoted by Ali Usman is no doubt a conservative estimate. It would be recalled that precisely 3,127 PWDs comprising turned out in Maiduguri, to receive the N30,000 grant disbursed by Governor Babagana Umara Zulum, in 2019, as part of of the social protection scheme of his administration.
Going by the 2019 figure, the number of PWDs reportedly affected by the September flood, therefore, doesn’t represent the full picture.
The affected PWDs were not invisible, but rather ignored—denied access to the evacuation routes and the dignity of urgent care. The stark numbers—37 deaths, 58 injured, 414,000 displaced—are a cold, clinical testament to the devastation. But beneath these statistics lies a deeper wound, one cut by marginalisation and neglect. “Already PWDs are facing marginalisation due to their disabilities, this flood disaster is a double blow for them,” lamented Ali Usman.
Corroborating him, Abiodun Tilawe, a social psychologist and emergency aid consultant stated that, “Persons with disabilities are usually at greater risk in an emergency. More worrisome, she argued, is the fate of older PWDs with mental health conditions. “They are at a higher risk of death as the hardships experienced impact devastatingly on their mental health. Many become traumatised by the fear of losing their lives and being left behind. From experience, older PWDs find it difficult to adapt to the extreme conditions into which they are suddenly thrust. Before the disaster, they are not taught about what to do to adapt and keep themselves safe. Some of them, who were displaced from their communities by protracted conflict, lived on the streets without any caregiver. Since the flood happened, they have been unaccounted for, and nobody has bothered to look for them,” said Tilawe.
Torrents of trauma: A visceral reality
For PWDs who survived, each day in the aftermath of the flood has been an agonising reminder of their vulnerability. The disaster stripped them of their already fragile autonomy. The very essence of disability is a barrier to mobility, access, and dignity—now amplified by the unrelenting ravage of nature.
For Jelani Aliyu, life as a PWD at the Gwange 3 temporary refuge, became extremely difficult. Confined to a wheelchair, the 81-year-old revealed that the damage done by the flood made accessing every basic necessity an impossible feat. According to him, the emergency shelters were not designed for PWDs. The aid distributions were chaotic – the strong elbowed out the weak, and the disabled were left to mope on the fringes. There were no ramps, no accessible toilets, no accommodations made for people like him. He was invisible.
Yet if nature’s fury alone were not enough, the ongoing conflict in the region cast an even darker shadow over the lives of PWDs. In 2014, in the town of Damasak, Mohamadou, a blind man of 53 years, fled from his home as Boko Haram laid siege to his community. Blind and defenseless, he clung to his wife and son as they swam across the treacherous Yobe River, ducking a volley of gunshots from the rampaging terrorists. “We swam like fish,” he recalled, though he could not see the river that threatened to claim his life.
For two years, Mohamadou lived in a refugee camp, dependent on the kindness of his son and strangers. But his disability marked him as prey. In the lines for aid, his young son was frequently shoved aside by stronger, older men, and time after time, he returned empty-handed.
“I would wait in line with my young son to get aid, but adult refugees would kick children away, including my son. We were too weak to fight back and would often lose our turn and return without getting anything from the distribution,” he said.
Mohamadou, like so many PWDs displaced by both flood and conflict, became a ghost—present but unseen, alive but uncared for.

It’s a hard life for PWDs
Nigeria was affected by the worst floods in a decade between June and November 2022, according to the Internal Displacement Monitoring Centre (IDMC). The floods triggered over 2.4 million displacements, the highest disaster displacement figure in sub-Saharan Africa in 2022. Half of the displacements were reported in the southern state of Bayelsa in the Niger river delta, but Anambra and Kogi were also heavily affected. Displacement camps in the north-eastern state of Borno were also flooded, forcing thousands of people already displaced by conflict and violence to flee again. By comparison, floods triggered 166,000 displacements in 2023, a figure in line with the average of the past decade. By the end of 2023, 81,000 people were still living in internal displacement due to disasters, a more than ten-fold reduction compared to the end of 2022.
Disaster displacement, whether triggered by cyclones, wildfires, floods, or other hazards, is a growing global issue with particularly harsh consequences for PWDs, who have to endure heightened risks due to discrimination and barriers in accessing essential services.
In 2020 and 2021, the UN noted that older PWDs may encounter unique challenges during climate-related disasters, such as the Borno flood. Similarly, a 2021 report by Women in Displacement (WID) revealed that 27% of IDPs in northeast Nigeria have a disability—a figure that has increased since the insurgency. As a result, PWDs living in camps are disproportionately affected, and frequently excluded from key interventions.
According to the WHO’s 2018 World Disability Report, many PWDs in Nigeria, are disproportionately affected in a disaster, emergency, and conflict situations due to inaccessible evacuation, response, and recovery efforts. The WHO notes that they are more likely to be left behind or abandoned during evacuation in disasters and conflicts due to a lack of preparation and planning, as well as inaccessible facilities, services and transportation systems.
During floods, older PWDs would require greater assistance and additional time to evacuate, but they receive less support. Further findings revealed that most IDP camps are not accessible and people with disabilities get turned away from the emergency shelters, oftentimes, due to a perception that they need “complex medical” services. Consequently, older PWDs find themselves at greater risk as they are more likely to suffer medical conditions – such as heart or respiratory conditions – through extreme situations, according expert opinion. Older PWDs may also take medications that cause intolerance and impair the body’s response to cold and heat. The staggering death rates of people with disabilities and older people during the 2021 heatwaves in British Columbia (BC), Canada, illustrates these points: 91 percent of those who died had a chronic medical condition or a disability and 90 percent were older people.
Due to the lack of accurate data, it is often unclear exactly how many people with disabilities and older people are affected by a particular disaster as indicated by the Borno flood. The lack of accurate data on the number of IDPs living with a disability and their location equally poses challenges to monitoring their needs and allocating resources. It also makes it difficult to tailor support and assess the inclusivity of responses over long term recovery and reconstruction efforts.
About a billion people, or 15 per cent of the globe’s population, are estimated to have a disability, of whom 80 per cent live in low- and middle-income countries, according to the Internal Displacement Monitoring Centre (IDMC). The global number of people with disabilities is increasing, partly because of ageing populations and a rise in chronic health conditions. It is not known how many people with disabilities live in IDP camps associated with disasters. The IDMC estimates that 5.1 million people were still displaced as a result of disasters at the end of 2019, but this figure is highly conservative. This is because data on the number of people living in displacement after a disaster event is scarce.
Accessibility issues, stigmatisation and variations in definitions tend to render IDPs with disabilities invisible during data collection. They are, as a result, often under-identified. For example, when Ambae Island in Vanuatu was evacuated in 2017 because of increased volcanic activity, there were concerns that a significant number of people with disabilities had not been identified among the evacuees. The International Organization for Migration’s Displacement Tracking Matrix (IOM-DTM) reported 37 people with disabilities out of 5,125 people located in one evacuation centre. This represented less than one per cent of the total displaced population. Sources vary on the prevalence of disability in Vanuatu, but 2019 data from the UN placed it at up to 12 per cent.

Disability Bill: Rosy in print, pale in execution
On January 23, 2019, Nigeria’s former President Muhammadu Buhari signed into law the Discrimination Against Persons with Disabilities (Prohibition) Act, 2018, following nine years of relentless advocacy by disability rights groups and activists.
The law prohibits discrimination on the basis of disability and imposes sanctions including fines and prison sentences on those who contravene it. It also stipulates a five-year transitional period for modifying public buildings, structures, and automobiles to make them accessible and usable for people with disabilities.
The law also established a National Commission for Persons with Disabilities (NCPD) in 2020. The NCPWD, tasked to guarantee PWDs access to housing, education, and healthcare, is also empowered to receive complaints of rights violations and support victims to seek legal redress amongst other duties.
Yet, one thing the NCPWD hasn’t done is to ensure the protection of Nigerians with disabilities during a natural disaster, emergency or conflict.
Lack of data, conflicting PWDs figures accentuate social
exclusion
Quoting recent World Health Organisation (WHO) figures, the immediate past executive secretary of the NCPWD, James Lalu, disclosed that currently, there are over 35.1 million persons living with disabilities in Nigeria of which a paltry 4,000 are duly registered.
Notwithstanding, his successor and incumbent executive secretary of the Commission, has reiterated the NCPWD’s commitment to ensuring inclusive policies for all clusters of PWDs in line with the Renewed Hope agenda of the incumbent administration of President Bola Tinubu.
Gufwan, made the assurance in Abuja during a parley with a delegation from the Pioneers of the Nigerian National and International Disability Civil Rights Movement and Policy Chapters, a disability advocacy Group.
“We are open to partnering with National and International bodies to ensure that the rights and privileges of persons with disabilities are protected as stipulated by the prohibition Act, 2018” he said.
Earlier, Gufwan affirmed that data remains a veritable tool for proper planning and executions of all disability inclusive projects in Nigeria.
The NCPWD had previously emphasised the importance of accurate data gathering and processing as the fundamental aspect of inclusive social policies for PWDs. “We must prioritise facts and figures of various clusters in the disability community in order to get it right,” he said, insisting that the need to ascertain the actual number of persons with disabilities is pertinent. “Over the years, persons with disabilities are believed to be about 35.1 million in Nigeria which is of course, a staggering figure but, we must revisit this and ascertain the authenticity of this figure and update it if necessary,” he said.
A 2018 estimate by the National Population Commission (NPC) states that there are about 19 million – that is, 9.6 per cent of 198 million-population approximately – living in Nigeria.
In Nigeria, social protection for PWDs remains weak, despite government claims of increased provisioning for them. The Discrimination Against Persons with Disabilities (Prohibition) Act, passed only after years of advocacy, has done little to address the deep-rooted exclusion PWDs face in society. Discrimination persists, driven by negative perceptions and cultural stigmas that label disabled individuals as cursed, especially in communities lacking proper disability-inclusive governance.
This exclusion often results in poverty, dependence on others, and health challenges. In the conflict-ridden northeast, PWDs, particularly women and children, suffer more acutely, being unable to pursue livelihoods or enjoy basic social rights.
A report by the Grassroots Researchers Associations (GRA) -authored by written by Timothy Ali Yohanna – revealed that PWDs in northeast Nigeria suffer frequent violations of their rights. These include opposition to marriages with non-disabled individuals, denial of medical care due to financial constraints, denial of access to decent shelter, and exclusion from social opportunities.
More worrisome is the institutionalised disregard of their right to life as established prior to, during, and in the aftermath of the Borno flood. These discriminatory practices and lack of disability-inclusive policies rendered PWDs particularly vulnerable during the disaster, further deepening their already precarious situation.

Beyond the Storm: A call for inclusion
Whether fleeing an extreme weather event or conflict, “disabled people are among the most vulnerable, and are more likely to be side-lined in every aspect of the humanitarian assistance process,” said Cheick Ba, Norwegian Refugee Council (NRC)’s Country Director in Nigeria, in the wake of Mohamadou’s predicament.
“They face multiple barriers in accessing aid, information, healthcare and protection. We, humanitarians, must do much better in our work. We have to systematically identify and register displaced persons with disabilities,” said Ba.
Article 11 of the United Nations Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities in risk and humanitarian emergencies, pays particular attention to the obligation of States and parties to undertake “all necessary measures to ensure the protection and safety of persons with disabilities in situations of risk, including situations of armed conflict, humanitarian emergencies and the occurrence of natural disasters.”
Environmental dangers and natural disasters like the Borno flood, can lead to the onset of many types of disabilities, and inaccessible environments prevent persons with disabilities from taking part in social and economic recovery. Rehabilitation and reconstruction efforts, therefore, must not only be inclusive and responsive to the needs of all people, including PWDs, but should include the latter’s participation, to ensure that their needs and rights are respected.
Women with disabilities, Aji, are a particularly vulnerable group whose needs should be included at all stages of recovery and reconstruction efforts.
But that is in the long run, in the short run, their survival depends on the goodwill of neighbours and family – those who dare look their way, not to scorn their ordeal or simply talk eyes to their grief.
As the waters recede and Maiduguri takes stock of the damage, there is a sense of loss so profound it is hard to put into words. Lives have been shattered, homes destroyed, communities torn apart. But amid the wreckage, there is also a spirit of resilience, as elderly PWDs are left adrift, far from the government’s reconstruction plans.
In the absence of government support, Zara Aji, for instance has learnt to take each day as it comes. In the waning light of day, she lounges on the broken veranda of what was once her home.
At her last encounter with the reporter, giant houseflies buzzed lazily in the thick air, around her, their tiny, winged bodies hovering over her face as if drawn to the scent of her sorrow. They alighted on her eyelids, her cheeks, her lips—silent witnesses to the desolation that had swept through her life. She did not flinch. She did not swat them away. Instead, she sat in stoic, heartbreaking inaction, allowing the flies to do as they pleased. Their buzzing filled the air with a strange, almost haunting hum, as though they too, mourned the loss she had endured.
For Zara Aji, there is no going back to what was. The flood has changed everything. On several days, she relives through the darkness of her existence, that fateful night in September, when the skies over Maiduguri wept with a fury rarely seen, and the Alau Dam collapsed, spilling its contents into the vulnerable heart of Borno, submerging the homes and lives of its people. Gwange, the neighbourhood where she had lived for years, was now a shell of itself—a landscape drowned in mud and sorrow.
Aji, at 83 and visually impaired, could not see the destruction around her. But she could feel it in the cold touch of the air, the dampness that clung to her skin, and the hollow echo of the neighbourhood’s once-familiar sounds.
Her frail, fragile memories remain a quiet witness to the horror of the reptilian flood that invaded her home, threatening to drown her. Aji was drowning, but salvation came on the back of her grandson’s love, in a poignant moment that whispered of a debt long owed and finally repaid.
Insight
If I should die giving birth: How Anita Nathaniel woke up during caeserian section, died in agony
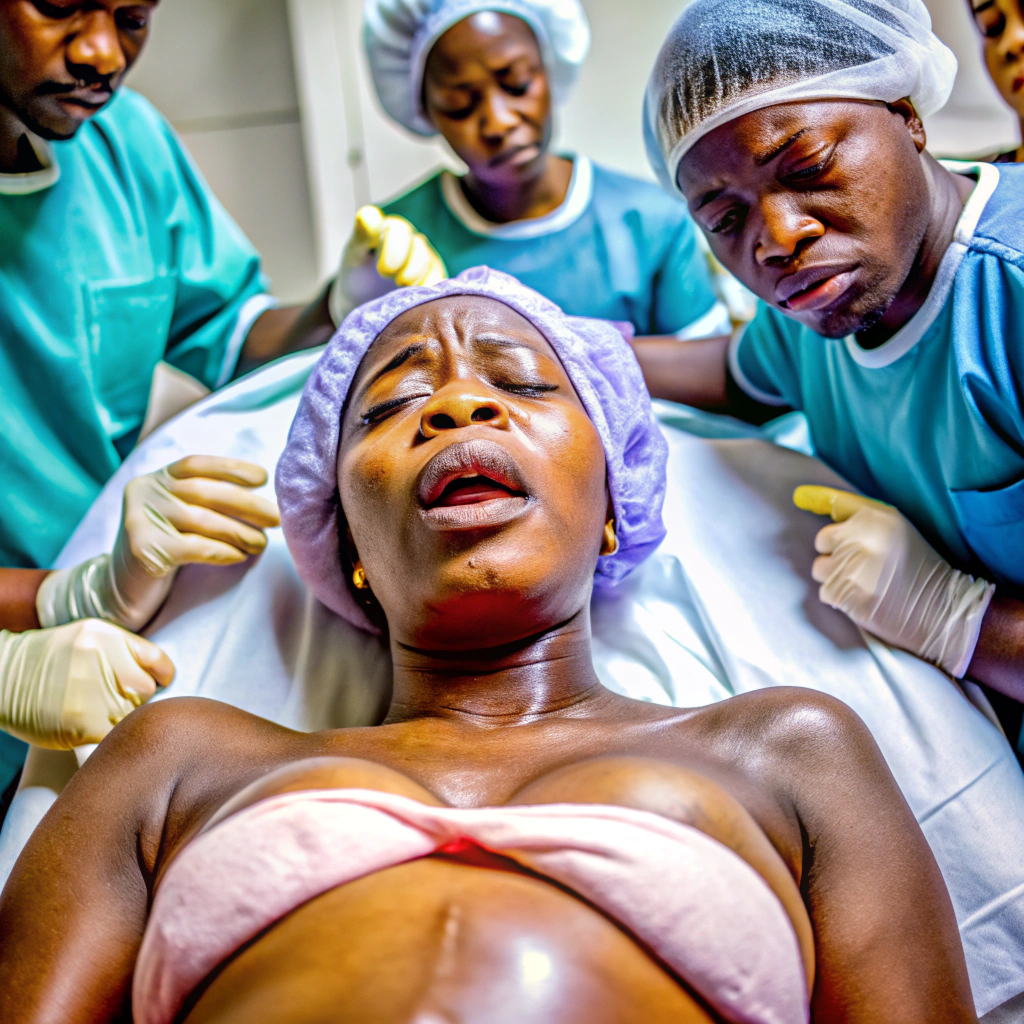
- Young, pregnant, dead: Inside the deathly maternity wards of City of Salvation Hospital
- Shady: Lagos hospital issues Ogun death certificate to victim of botched surgery, doctors medical records
- Why dead mothers, injured wives litter Nigeria’s labour rooms
By Olatunji OLOLADE, Associate Editor
Anita Nathaniel lay tethered to the surgical table, captive between life and death. There, beneath the stern glare of fluorescent lights, inside the City of Salvation Hospital, Egbeda, Lagos, a frantic opera unfurled, echoing the sombre notes that would cast her fate in a dark shroud.
Inside the medical theatre, an electronic speaker belched gospel song that whirled like a dirge through the air. “I surrender to you! I surrender to you!” the speaker blared.
Amid the cacophonous peal of faith and surrender, Anita stirred to the sharp intrusion of a knife cutting through her belly. Barely one minute into the caesarean section that would bring her child into the world, the haze of anaesthesia receded, and the cutting pain of the surgeon’s blade sliced through her body. As the scalpel grazed her abdomen, the world around her faded into a hazy abstraction, leaving only the visceral torture of the procedure.
With every thrust of the surgeon’s hands, gobs of flesh and innards were yanked aside in reckless abandon. And the theatre erupted in a carnage of blood and gore, as the colour red splattered in stark contrast against the sterile white of the sheets.

Late Anita
Anita gasped. Then she wailed: “Aargh! What are you doing to me? Stop! Don’t do that! Please, don’t do that! Jesus, please save me. I am in pain! Aargh! Aargh!” Her voice, ragged with agony, was met with chilling indifference. A voice, detached and careless, tossed a dispassionate word back into the abyss of her suffering: “Sorry.”
Yet, the knife did not pause. The hands of Dr. Okusanya Abimbola pressed on, pulling and tearing, parting her flesh roughshod, scraping through her insides as though her pain was no more than the distant chirp of a cricket at dawn. As the surgeon’s hands dug deeper, Anita’s wails faded, swallowed by the clatter that enveloped the room like a funeral shroud, leaving only the refrain of the gospel song playing jarringly in the background: “I surrender to you, I surrender to you.” But in that theatre, it wasn’t Anita’s soul surrendering to divinity, the 32-year-old surrendered to the brute spunk of negligence.
In the aftermath of that grisly ballet…
As the surgeon extracted the child from the ruins of the mother’s body, the air grew thick with a haunting stillness. Anita lay there, a broken vessel. Silence fell over her, like a shroud more tangible than the bloodied sheet that lay across her lifeless form. Was she gone? Or was she merely suspended in the throes of death, her spirit fighting to escape surgical torture? These questions lingered, unanswered, in the hushed theatre.
To the casual observer, the tableau was unthinkable—a macabre circus of sloppiness, where the doctor and his nursing assistant plowed Anita’s innards and tore through her flesh. A large wad of cotton wool was shoved into her gaping wound, and recklessly pulled out, in a futile effort to stanch the torrents of blood that gushed from her belly.
“I saw a nurse bring out three big bowls of blood during the operation,” recounted Evwiarivi Nathaniel, Anita’s husband, his voice quaking with unbearable grief. “I asked her what she intended to do with it, and she said she was going to pour it away,” said the chef and native of Ikeresan, Sapele, Delta State.
From the moment the theatre doors swung open, what followed was a scene bathed in confusion. Nurses scurried out of the operating room, their faces tense, yet they assured Nathaniel that, “Everything is fine.” But their restless feet told a different story. The minutes stretched into hours, each one more suffocating than the last, until finally, one of the nurses emerged with the fruit of Anita’s labour: her child, Jaden.
Nathaniel enquired about his wife, and the nurse replied that she was fine. “She said that I should just hold on to my new born baby,” he said, revealing his disappointment that the hospital had no baby cot to keep the child. Nathaniel’s heart clung to the newborn in his arms, but his wife’s absence gnawed at his spirit. “She’s fine,” resounded the assurance, hollow in its echo.
Time passed, too much time, and then, the truth hurtled from a nurse’s lips, like a dagger through his chest. Anita was gone. His beloved wife had bled out, distressed and lonely, on the surgical table.

Under the blade of silence
Until her death, Anita had cut a perfect picture of good health. Her antenatal checkups had shown no sign of complications even as her vitals echoed with promise of a safe delivery. “She couldn’t wait to birth our first child,” disclosed Nathaniel. But fate, draped in the sterile white of a surgical gown, had other plans.
Indeed, the City of Salvation Hospital was no stranger to Anita. Its cold halls had witnessed her belaboured plod through the delicate dance of pregnancy, each antenatal visit a rehearsal for the grand performance of birth. Yet when her water broke at 1:00 am on August 15, 2023, the future shimmered with hope and an undercurrent of unease. Nathaniel called the hospital but a nurse’s voice, seemingly draped in the sluggishness of night, urged him to wait till daybreak before he brought Anita in. But spurred by excitement and first-time naivety, Nathaniel spirited his wife to the clinic at 4:30 am. His heart heavy with anticipation and a subtle, creeping dread.
On getting to the hospital, a scan was conducted on Anita to determine the progression of her labour. But the 32-year-old was far from the image of fragility one might expect. She walked, she climbed stairs, did squats, guided by the nurse’s calm instructions. Her body, full of life, seemed ready for the gruelling birthing process ahead.
“At 9:00 am the nurse took my wife to run a scan, when the result was out, I took the result and scanned it to my brother, Amos Evwiarivi, so he could show his doctor friends to ascertain if everything was alright. My brother thereafter confirmed to me that his doctor friend said from the scan, everything was okay,” said Nathaniel. But this was a temporary salve to his growing unease – for soon, Ifedolu Oreitan, a nurse playing the role of a “resident doctor,” cast a shadow over the morning with his sudden suggestion of a caesarean section. Oreitan subsequently admitted in a court deposition that he examined Anita and concluded that the baby would be best delivered via a caesarean section. “I made my recommendation for c-section around 9:00 am that same day of August 15, 2023.” This was yet another interesting episode in the build up to the tragedy as Oreitan, being a nurse, lacked the professional and ethical capacity to recommend a procedure that was best determined by a qualified obstetric surgeon.
Nathaniel refused, stressing that he and his wife wanted her to have a normal vaginal delivery. Neither the innuendo of complicated labour or death scared Anita, in particular. And so, they waited. Anita, though now tethered to the hospital bed by a drip, seemed a pillar of strength. But as time stretched, her moans of discomfort grew intense, the pain writhing in her like a snake coiled in her belly.
Oreitan returned, more insistent now, his words ringing with an urgency that Nathaniel could not ignore. With his wife’s agony more evident, Nathaniel relented and paid N150,000 of a N300, 000 surgical bill. “After making the payment, I was assured that the surgeon would join them shortly. But my wife had to wait for well over eight hours before the surgeon arrived,” said Nathaniel.
The attending surgeon, Dr. Abimbola did not appear until late in the afternoon, he said. And when he finally did, it wasn’t with the air of urgency or in the careful assembly of a skilled team, but with Nurse Oreitan, and two auxiliary nurses. This was a flagrant violation of medical personnel specifications for a caeserean section: One obstetric surgeon, one assistant surgeon, an anaesthesiologist, a paediatrician, and two qualified nurses.
In the City of Salvation Hospital’s medical theatre, the crucial figure of an anesthesiologist was missing, an omission that would become the linchpin in the unfolding tragedy.
Although, Anita walked into the theatre by herself, hoping to reemerge hale and hearty with her baby, she didn’t. After waiting for a while one of their nurses came out and broke the sad news of her death to her husband. “It was traumatising for me. I became miserable and heartbroken, knowing my child had become motherless and left without motherly love,” said Nathaniel.
By the time his wife breathed her last, however, the dubious gear of deception was in full swing. A death certificate, hastily issued by the Ogun State Health Board—hundreds of miles from where Anita drew her last breath was handed to her husband, Nathaniel. The certificate, a pale slip of paper meant to account for Anita’s sudden death, raised more questions instead. Why an Ogun State death certificate, when Anita had died in Lagos? The answers lay in a cover-up meticulously crafted by the hospital.
What Anita experienced in her final hours
In Anita’s final moments, the anaesthesia evidently failed to maintain the necessary depth of unconsciousness, thus causing her to wake feel intense pain as the surgeon cut into her abdomen and manipulated her internal organs. Her body’s natural response to such extreme pain was to activate the fight or flight mechanism, increasing her heart rate, blood pressure, and stress hormone levels. However, in a patient weakened by childbirth, this physiological response can be dangerous. The massive loss of blood and initial surge in blood pressure (hypertension) could have caused damage, but as the surgery progressed and her blood loss increased, her blood pressure would have dropped dangerously low (hypotension). This hypotension reduced blood flow to vital organs, including the heart, kidneys, and brain, leading to potential organ failure, and subsequent death, argued an obstetric surgeon with a Lagos based university teaching hospital, who pleaded anonymity.
In other words, as the cold blade of the scalpel pierced the thin veil of Anita’s flesh, she should have been lost in the deep, dreamless sleep that “general anesthesia” promises—a twilight where pain and fear do not tread. But the anesthetic, meant to keep pain at bay, had thinned away, leaving her vulnerable to the sharp, unsparing stab of the surgeon’s blade.
When her eyes fluttered open on the surgical table, Anita must have felt like a lamb betrayed by its shepherd, waking to the jaws of a ravenous wolf. The searing agony that coursed through her veins was not just the sting of the incision, but the excruciating sensation of her flesh being parted, layer by tender layer, while her consciousness was trapped in a body that could not cry out, that could not flee. The nerves in her abdomen screamed in violent protest, sending shockwaves of unbearable pain into her spine, her limbs, her very soul. Her mind, swimming in the confusion of half-wakefulness, must have wrestled with the agony of it all—unable to comprehend how she could still feel, still hurt, while the very essence of life bled away from her. Hence her initial plea and wailing of being in pain.
Anita’s final moments were not just a medical catastrophe—they were an unutterable violation of the sanctity of life, a tearing of her soul from her body while still tethered to the torturous sensations of mortality. The surgeon, while doubling as an anesthetist, evidently lacked the competence to shield her from pain. Thus on his watch, Anita’s body, once a vessel of life and creation, became a crucible of unimaginable torment and death.

The grim statistics
Anita’s tragic fate unfurled as yet another thread in the fabric of Nigeria’s maternal mortality conundrum, a grim statistic that haunts the hospital corridors of a nation grappling with the spectre of death. Nigeria holds the tragic title of one of the highest maternal mortality rates in the world. In 2020 alone, around 82,000 women succumbed to the perils of childbirth—each death a cruel reminder of a broken healthcare system, marred by neglect and incompetence.
Amidst this tragedy, the statistics loom ominously. Nigeria’s maternal mortality rate stands at a staggering 1,047 deaths per 100,000 births, a haunting figure that casts a long shadow over the aspirations of countless mothers.
“The causes of death included severe hemorrhage, high blood pressure, unsafe abortion, and obstructed labor,” reports the World Health Organization (WHO, 2020), illuminating the harrowing reality that women like Anita face daily. With only one doctor available for every 4,000-5,000 patients, the lack of care transforms the act of childbirth into a roll of the dice—a gamble where the stakes are life and death.
Anita, in her tragic demise, further illustrates the chaos emblematic of Nigeria’s deathly maternity wards – nurses scurrying in disarray, desperately seeking medications that never arrived, leaving her vulnerable and alone in her hour of need.
How City of Salvation Sought to Bury Anita Nathaniel’s Death
An autopsy conducted by the Lagos State University Teaching Hospital (LASUTH) unveiled chilling truths. While the medical team sought to attribute Anita’s death to heart failure, it was discovered that the records had been manipulated. Blood pressure readings, once steady, were altered in a desperate attempt to cover the traces of malpractice that led to his wife’s demise.
The ink marks on the charts, a testament to the deceit, revealed the extent to which the medical personnel conspired to obscure the truth. “The blood pressure initially recorded for my late wife was 110/70,” he noted with bitter clarity, “but upon her death, it was changed to 170/120.”
Investigators from the Nigeria Police Force, led by Investigating Police Officer (IPO), SP Hauwa Idris Adamu, visited the hospital in search of the truth. What they found, however, was a litany of anomalies— there was no anesthesiologist, no pediatrician, no assistant surgeon. Dr. Abimbola had conducted the surgery without a qualified team.
“Instead of referring the deceased to a General Hospital for better care, the suspect (Dr. Abimbola) made a trial-by-error approach. The issuance of an Ogun State Health Board Death Certificate instead of one from Lagos State, where the hospital is located, raised concerns,” according to the IPO’s report.
The hospital itself became a scene of concealment. Key documents, including Anita’s antenatal records, vanished into thin air. The files that remained had been tampered with, manipulated in a desperate attempt to erase the hospital’s role in her death.
The hospital management claimed they were safeguarding the files, which further deepened the investigators’ concerns. The management, when confronted, offered nothing but vague explanations.
Although the hospital was sealed by the Health Facility Monitoring and Accreditation Agency (HEFAMAA), in the wake of the incident last year, findings further revealed that HEFAMAA conveniently turned a blind eye as the City of Salvation Hospital resumed operations amid a frantic makeover of its hitherto derelict facilities. Evidence crucial to the investigation of Anita’s death disappeared. When the police returned for a second inspection, the scene had been tainted, the clues to Anita’s death now swallowed in a haze of hasty renovation.
In the aftermath of Anita’s death, the police arrested Nurse Oreitan, whose role in the operating room was deemed inappropriate and illegal. And then, there was Dr. Abimbola—the man whose hands had wielded the scalpel and whom the police identified as the principal suspect. He came forward, but not as one burdened with guilt. He arrived at the police station on October 19, 2023 (almost two months after the incident) flanked by lawyers. He was subsequently charged and made a voluntary statement.
Attempts to speak with Dr. Abimbola have so far been unproductive. Since Tuesday, September 24, he has repeatedly spurned attempts to interview him, ignoring five successful calls to his phone at 12:10 pm, 12:11 pm, 12:27 pm, 12:29 pm and 13:24 pm, respectively. At the fifth try, he switched off his phone, and subsequently ignored a message and request for an interview over late Anita’s botched C-section.
On Friday, September 27, more calls were placed to his second phone number, but having answered the call, he ended it abruptly, just after identifying that he was Dr. Okusanya Abimbola. Subsequently, five successful calls were placed to his line at 9:30 am, 9:31 am, 9:32 am, 9:33 am and 9:38 am, respectively. Then a message was sent to his line – which also bears an associated identity with Atlas Medicare – via normal SMS route and WhatsApp at exactly 9:42 am, establishing that he had repeatedly ignored the news medium’s calls.
To this he sent the terse response: “Good morning Sir/Ma. I have received your message. Will respond to you shortly via WhatsApp.” Even though The Nation sent him a couple of questions, urging him to respond to allegations made against him by Nathaniel and the City of Salvation Hospital, Dr. Abimbola failed to respond.
However, a perusal of his court deposition revealed that Dr. Abimbola, like his former employer, the City of Salvation Hospital, seeks absolution from liability for Anita’s botched surgery and subsequent death.
Abimbola, who until his sack, was the Medical Director of City of Salvation Hospital, held that late Anita presented with high blood pressure (170/120 mm Hg), eclampsia. And that despite the doctor (Nurse Oreitan)’s advice for an elective caeserian section, she and her husband declined, opting for a vaginal delivery based on their faith. “They also declined admission saying that they will apply their faith and pray for a vaginal delivery,” he said.
Dr Abimbola claimed that he already booked for an anaesthesiologist but the couple’s delay in agreeing to a C-Section prevented the former from being part of the surgery – thus establishing that the hospital had no in-house anaesthesiologist.
He said, “When I weighed the consequences of a further delay, I decided to go ahead with the C-Section in the hope of saving the life of the mother and her baby. I opted for a mild general anaesthetic since there was no one to give the deceased spinal anaesthesia. The dosage was subliminal since I did not want her BP (Blood Pressure) to shoot up. The baby came out very weak and floppy but responded to resuscitation. Suddenly SPO2 (Saturated Percentage of Oxygen) was noticed to be dropping and the deceased stopped breathing. CPR (Cardio Pulmonary Resuscitation) was commenced immediately. All efforts at resuscitation proved unfruitful and abortive. I pronounced her dead at about 4pm. In my opinion, the cause of death was intra op of complications of eclampsia which resulted from the delay in performing the CS due to the delay in giving consent.” Dr. Abimbola, however, claimed that he performed the C-Section on late Anita “professionally and diligently” to the best of his ability and training as a medical doctor.

Hospital ducks liability, accuses sacked surgeon of culpability
At The Nation’s visit to the City of Salvation Hospital in Egbeda, it was discovered that Dr. Abimbola, has been sacked. The nursing staff murmured that every nurse who stood by him in that fatal surgery had also been dismissed, as if their mere presence could resurrect the spectre of their errors.
Speaking with The Nation, the hospital’s current Medical Director, Dr. Adeyiwolu Damilare, hinted at the failures of his predecessor. In a subtle disclaimer, he stated that, “A doctor must approach and recognise each case as a peculiar one. He must be cautious in handling cases. What if the patient is his blood relative, he would take extra care, won’t he? If the woman (late Anita) walked in with her two legs, are you, as the doctor saying you don’t know when to intervene and how to intervene? If you take the vitals and you see that you don’t have the facilities to manage her case, the next thing for you to do as the doctor is to get a quick intervention,” he said.
According to him, immediately a doctor realises that a patient’s case is beyond his facility, he must seek emergency intervention from a more equipped facility. “That is when you know a good doctor. We know when a patient’s case is going to deteriorate. We know if we have the equipment to manage it or not. When you give an anaesthetic agent, you factor in the weight and body mass of the patient. This would determine the degree of anaesthesic agent that will be used on the patient. Someone with greater body fat or mass would require greater quantity to prevent it from wearing off earlier. Once it wears off on your patient and you see that you are not done with the surgery, you look at the blood pressure and it is hitting the roof, you shouldn’t administer anaesthesia on the patient again, because if you do, it’s going to cause a hypertensive emergency.”
With a pastoral calm that belied the tragedy, Pastor Abel, the hospital’s spiritual overseer, argued that, “This is not between the hospital and the Nathaniel family. The matter lies between Dr. Abimbola and the Nathaniels,” he said. His words, like a feeble prayer, sought to absolve the hospital of guilt against the weight of the facts: the surgery, the negligence, the tragic end—all that transpired under the hospital’s roof.
The standard practice for caeserian section
Dr. Habeebah Ishaq, a UK-based Consultant Paediatrician and former staff of Reddington Hospital, explained that Anita’s death likely resulted from a broken or damaged blood vessel, possibly due to accidental ligation of a blood vessel. She emphasised that a proper caesarean section requires at least two doctors—one lead surgeon and an assistant—along with a qualified anesthetist, an assistant anesthetist, and one or two trained nurses, not auxiliary nurses. She described it as criminal negligence that only one doctor, one nursing assistant, and auxiliary nurses performed Anita’s surgery, arguing that an anesthetist could have alleviated Anita’s pain instead of relying on one person acting as both surgeon and anesthetist.
She clarified that the surgeon’s role is to operate and ensure the mother’s safety, while managing pain and anesthesia is the anesthetist’s responsibility, and that Anita’s waking up during surgery indicated a failure in proper anesthesia administration.
Dr. Ishaq explained that the standard practice for caesarean sections is to use spinal anesthesia, which numbs the lower body without putting the patient to sleep. General anesthesia is only used in cases of complications during labour where there is an immediate threat to the baby’s life. Proper general anesthesia would have kept Anita unconscious throughout the surgery and into recovery, preventing her from waking prematurely, she said.
The shortage of skilled anaesthesiologists in Nigeria is a significant contributor to the country’s high maternal mortality rate, especially among women undergoing Caesarean sections (CS). Anaesthesiologists play a vital role in ensuring the safety of women during surgery by managing pain and preventing complications.
Anaesthetists have knowledge of acute physiology and are adept at fluid management, invasive monitoring and other aspects of intensive care, thus, they are an integral part of the team managing obstetric complications, including the critically ill mother with obstetric haemorrhage, sepsis or eclampsia, according to Prof. Elizabeth Ogboli-Nwasor, of the Department of Anaesthesia, Ahmadu Bello University Teaching Hospital, Zaria, Kaduna.
On her part, Dr. Bisola Onajin-Obembe, the President of The Global Alliance of Surgical, Obstetric, Trauma, and Anesthesia Care (G4 Alliance), emphasised the need to address the critical shortage of anesthesia providers in Africa. Though the continent houses nearly 17% of the global population, most people lack access to safe anesthesia services due to a dire shortfall in trained professionals. For instance, while the U.S. has around 20 anesthesiologists per 100,000 people, Nigeria averages only 0.58. This disparity, according to her, highlights the global anesthesia workforce crisis, with sub-Saharan Africa particularly falling far below the recommended four anesthetists per 100,000 population. By 2030, the region will need more than 300,000 additional anesthesiologists.
Drawing from her extensive experience as a lead consultant anesthesiologist at the University of Port Harcourt Teaching Hospital and her involvement in Nigeria’s National Surgical, Obstetrics, Anaesthesia, and Nursing Plan (NSOANP), she advocated recently, for an in-depth understanding of regional healthcare systems, emphasising the need for strategic planning, collaboration with established institutions to create effective training programs. She noted that partnerships with entities like the University of Global Health Equity and the G4 Alliance are crucial to enhancing health equity and leadership in anesthesia.
But that is in the longrun, in the shortrun, thousands of pregnant Nigerian women will continue to prowl the dim corridors of private medical facilities, like the City of Salvation Hospital – where they may be subjected to the mercy of arbitrary elements.
One year after, the hospital’s corridors stay dimmed by the veil of silence hastily drawn over sordid details of the newly married bride and first-time mother’s tragic demise.
The truth, however, is as fragile as the 32-year-old’s final breath, and stays buried beneath layers of excuses. As Nathaniel, the deceased’s widower, grapples with her loss, he is bent on securing justice against the hospital and the medical personnel deemed liable for her botched surgery. So doing, he hopes to inspire many who had suffered a similar fate to seek redress. Besides filing a petition for an inquest into the suspicious death of his wife, he has also instituted legal action against the hospital and the personnel deemed complicit.
To Nathaniel, Anita’s death was no mere happenstance of fate, but a grievous wound carved by mortal hands—by a system that cloaked itself in promises of sanctuary, only to surrender her to death’s unfeeling embrace. It was not nature that claimed her, but negligence draped in white coats.
For the 37-year-old, moving forward is a pilgrimage through grief and struggle. He fights for justice with trembling resolve, even as he shoulders the weight of fatherhood alone, tending to his 13-month-old son, Jaden, who knows nothing of the motherless world he has been born into.
Each day without her is a chasm that swallows Nathaniel whole—a void no measure of time can fill. And in the quiet shadows of the night, as he cradles his son to sleep, the echoes of that fateful day return to haunt him. He recalls the nurse’s hollow reassurance, the cruel illusion of safety, even as Anita lay bleeding out—her life ebbing away beneath the surgeon’s blade, her body cooling on the sterile altar of failed care.
-

 Uncategorized7 years ago
Uncategorized7 years agoThese ’90s fashion trends are making a comeback in 2017
-

 Uncategorized7 years ago
Uncategorized7 years agoAccording to Dior Couture, this taboo fashion accessory is back
-

 Uncategorized7 years ago
Uncategorized7 years agoThe final 6 ‘Game of Thrones’ episodes might feel like a full season
-

 Insight7 months ago
Insight7 months agoTinubu sacks two heads of govt agencies, picks replacements
-

 News10 months ago
News10 months agoNigeria Moves Up In Corruption Perception Index – TI
-

 Uncategorized7 years ago
Uncategorized7 years agoThe old and New Edition cast comes together to perform
-

 Uncategorized7 years ago
Uncategorized7 years agoUber and Lyft are finally available in all of New York State
-

 Insight6 months ago
Insight6 months agoWhere little boys die young






